Generative AI has transformed how organizations interact with data. However, deploying large language models alone is no longer enough. While LLMs generate fluent responses, they often lack accuracy, freshness, and enterprise context. Because of this, most production AI systems now rely on Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
That said, building a small RAG prototype is easy. Scaling it to handle millions of documents, thousands of users, and real-time requests is a completely different challenge.
Therefore, modern AI platforms require scalable RAG pipelines.
A scalable RAG pipeline ensures that retrieval, ranking, and generation remain fast, reliable, and cost-efficient, even under heavy workloads. As a result, organizations can move from experimental chatbots to enterprise-grade AI systems that run continuously and predictably.
This guide explains what scalable RAG pipelines are, why they matter in 2026, and how to design them step-by-step.
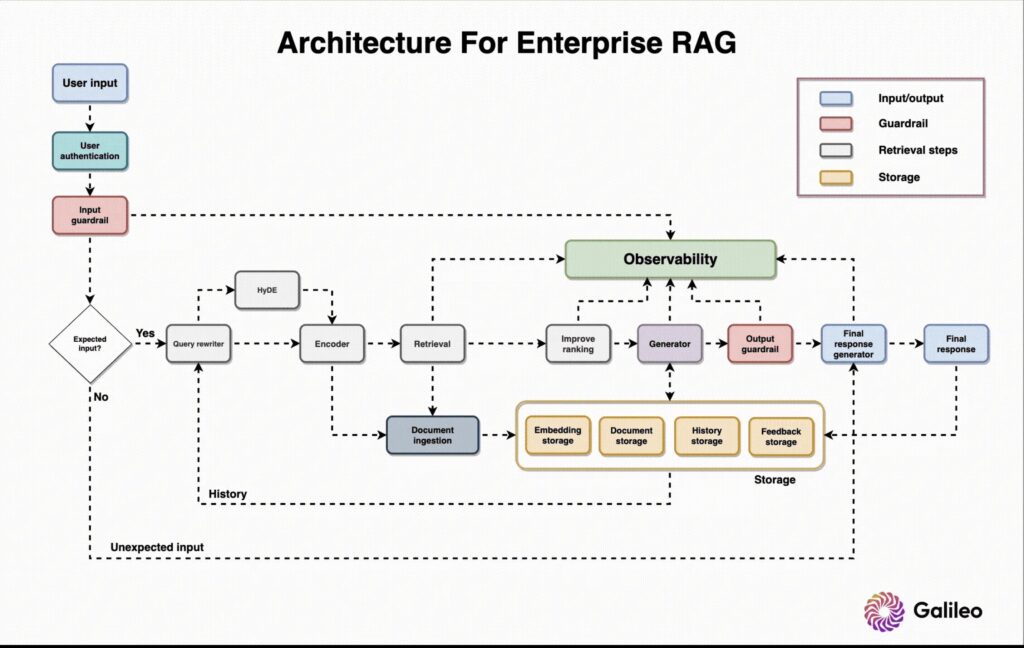
What Is a Scalable RAG Pipeline?
A scalable RAG pipeline is a system architecture that combines:
- Data ingestion
- Indexing
- Retrieval
- Ranking
- Context assembly
- AI generation
- Monitoring
Unlike basic RAG setups, scalable pipelines are designed to handle:
- Large datasets
- High concurrency
- Low latency
- Continuous updates
Therefore, scalability is not an add-on feature. Instead, it is a core architectural requirement.
Why Basic RAG Systems Fail at Scale
Initially, many teams build simple RAG systems using:
- One vector database
- One model call
- One retrieval step
However, this approach breaks quickly.
For example:
- Retrieval becomes slow with millions of documents
- Context becomes noisy and irrelevant
- Model costs increase dramatically
- Latency grows beyond acceptable limits
- System reliability drops
Because of these issues, organizations must redesign their systems using scalable pipeline architecture rather than monolithic flows.
A modern scalable RAG pipeline typically follows this structure:
- Data ingestion
- Preprocessing and chunking
- Indexing (keyword + vector)
- Intelligent retrieval
- Ranking and filtering
- Context assembly
- Model generation
- Validation and monitoring
Thus, each stage is modular and independently scalable.
Core Components of Scalable RAG Pipelines
1. Data Ingestion Layer
First of all, data must be ingested continuously.
This includes:
- Documents
- Databases
- APIs
- Knowledge bases
- Logs and records
However, ingestion cannot be manual. Therefore, scalable systems use automated pipelines that update indexes in real time.
As a result, AI responses always reflect the latest data.
2. Preprocessing and Chunking
Raw documents are rarely model-friendly. Because of this, preprocessing is essential.
This stage performs:
- Text cleaning
- Deduplication
- Chunking large documents
- Metadata tagging
Therefore, retrieval becomes faster and more precise.
Smaller, well-structured chunks significantly improve scalability.
3. Hybrid Indexing Layer
Next, data is indexed for fast retrieval.
Modern scalable systems use:
- Keyword indexes for precision
- Vector embeddings for semantic similarity
- Metadata filters for governance
Therefore, hybrid indexing ensures both accuracy and performance.
Relying only on vector search is often slow at scale. Consequently, hybrid approaches are more efficient.
4. Intelligent Retrieval Layer
After indexing, the system retrieves relevant content.
However, retrieving everything is inefficient. Therefore, scalable systems:
- Limit retrieval size
- Use query-aware strategies
- Apply filters early
- Cache frequent queries
As a result, latency remains low even with large datasets.
5. Ranking and Re-Ranking
Raw retrieval results often contain noise. Because of this, ranking becomes critical.
This stage:
- Scores relevance
- Removes duplicates
- Re-ranks using AI models
- Selects only top-k results
Therefore, only the most useful information is sent to the model.
Smaller context equals faster and cheaper inference.
6. Context Assembly
Next, retrieved content must be structured.
This includes:
- Ordering logically
- Compressing text
- Managing token limits
- Formatting prompts
As a result, the AI model receives clean and focused context, which improves output quality.
7. Generation Layer
At this stage, the language model generates responses.
However, scalable systems often use:
- Different models for different tasks
- Lightweight models for simple queries
- Heavy models for reasoning
Therefore, costs are optimized while maintaining performance.
8. Validation and Monitoring
Finally, production systems require observability.
This includes:
- Latency monitoring
- Retrieval accuracy tracking
- Cost measurement
- Response validation
- Logging and analytics
Without monitoring, scalability cannot be maintained.
Key Principles for Building Scalable RAG Pipelines
Modular Architecture
Each component should scale independently. Therefore, ingestion, retrieval, and generation must not be tightly coupled.
Caching Strategies
Frequent queries should be cached. As a result, response time decreases and costs drop significantly.
Context Minimization
More context does not mean better answers. Instead, smaller and more relevant context improves both speed and accuracy.
Horizontal Scaling
Distributed search engines and databases allow parallel processing. Therefore, systems can handle millions of documents efficiently.
Asynchronous Processing
Non-blocking workflows reduce latency. Consequently, user experience improves under heavy loads.
Common Use Cases
Scalable RAG pipelines are widely used in:
- Enterprise knowledge assistants
- Customer support automation
- Research platforms
- Compliance analysis
- Internal search systems
- AI copilots
In each case, scalability ensures consistent performance.
Challenges in Scaling RAG Systems
Despite their benefits, scalable pipelines introduce challenges.
For example:
- Index synchronization
- Vector search latency
- Token limitations
- Infrastructure costs
- Monitoring complexity
Therefore, careful architecture design is required from the beginning.
Best Practices in 2026
To build robust scalable RAG pipelines:
- Use hybrid search
- Limit retrieval size
- Separate retrieval and generation
- Cache aggressively
- Monitor continuously
- Optimize prompts
- Scale horizontally
Following these practices ensures stable long-term performance.
Future of Scalable RAG Pipelines
Looking ahead, scalable RAG pipelines will become more autonomous.
Future systems will include:
- Self-optimizing retrieval
- Adaptive ranking
- Multi-agent orchestration
- Real-time feedback loops
- Automated scaling
Therefore, RAG pipelines will evolve into intelligent infrastructure layers, not just AI features.
Final Thoughts
In 2026, building a simple RAG demo is easy. However, building a scalable RAG pipeline that handles real users and real data is what separates prototypes from production systems.
By focusing on:
- Modular design
- Efficient retrieval
- Controlled context
- Smart model usage
- Continuous monitoring
organizations can build AI systems that are fast, reliable, and future-proof.
Ultimately, scalable RAG pipelines are not optional — they are the foundation of modern enterprise AI architecture.