Artificial Intelligence has advanced rapidly, especially with the rise of large language models. However, despite their power, these models face a fundamental limitation: they generate answers based on probability, not verified knowledge. Because of this, hallucinations, outdated information, and lack of domain context remain serious challenges.
Therefore, modern AI systems are no longer built on standalone language models. Instead, they rely on Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) architecture.
In 2026, RAG architecture has become the standard foundation for building accurate, scalable, and trustworthy AI systems. Rather than depending only on model memory, RAG systems retrieve real data from external sources before generating responses.
As a result, AI systems become data-grounded, explainable, and enterprise-ready.
This article explains Retrieval Augmented Generation architecture, how it works, why it matters, and how modern systems are designed using this approach.
What Is Retrieval Augmented Generation Architecture?
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) architecture is a system design pattern that combines:
- Information retrieval
- Context augmentation
- AI-based generation
Instead of directly generating answers from a language model, the system first retrieves relevant real-world data and then uses that data to generate responses.
In simple terms:
Retrieve → Augment → Generate
Therefore, the AI model does not guess answers. Instead, it reasons over retrieved knowledge.
Why RAG Architecture Is Essential in 2026
Initially, AI systems were built using only pretrained models. However, several problems quickly emerged.
For example:
- Model knowledge becomes outdated
- Private data cannot be accessed
- Hallucinations reduce trust
- Compliance and governance become difficult
Because of these limitations, organizations needed a way to connect AI systems to live, trusted data sources.
Therefore, RAG architecture emerged as the solution.
Moreover, regulatory and enterprise requirements demand traceability and explainability, which RAG naturally supports.
As a result, RAG architecture is now the default design pattern for production AI systems.
High-Level RAG Architecture Flow


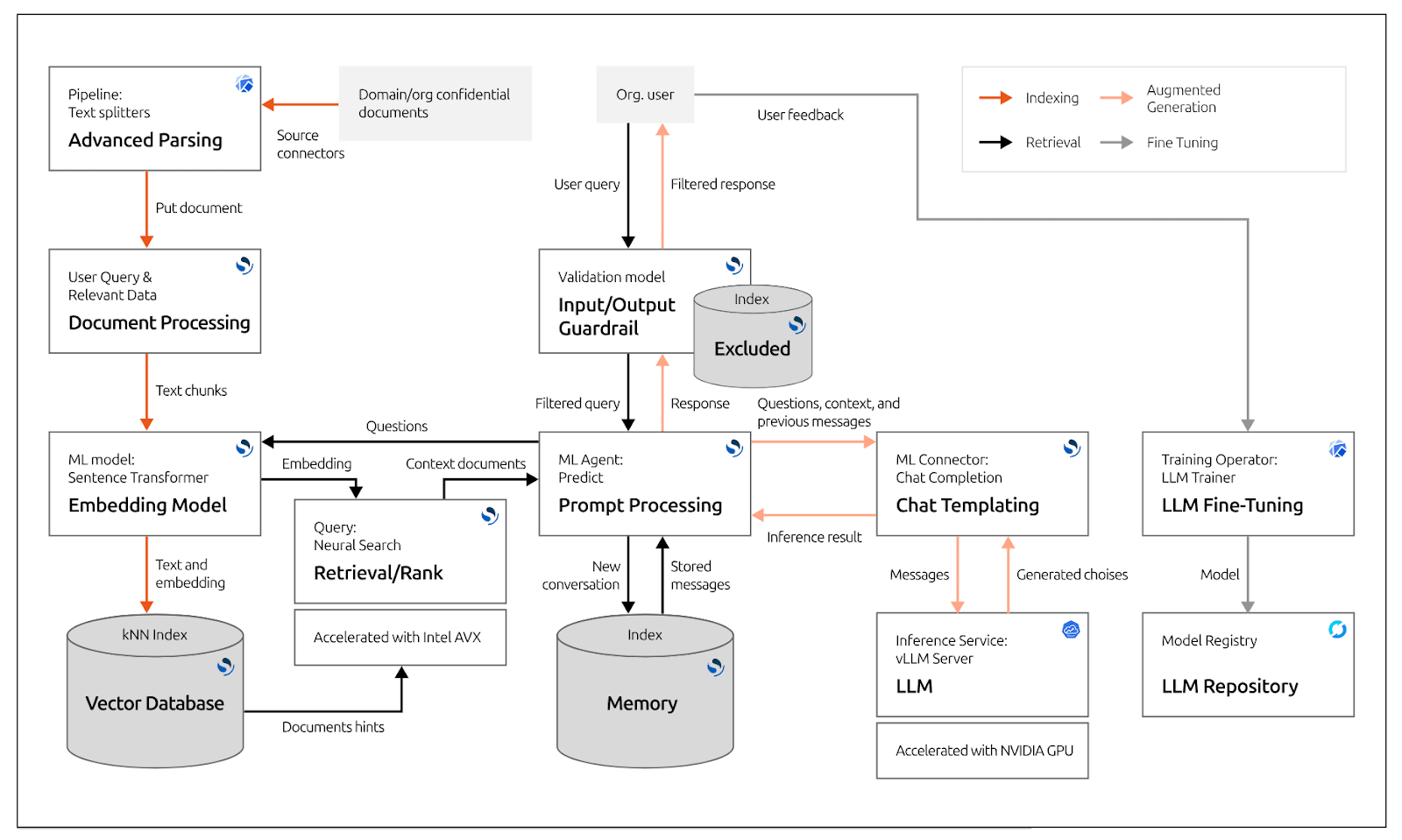
A modern RAG system follows this structured flow:
- User submits a query
- System analyzes intent
- Relevant data is retrieved from external sources
- Retrieved data is ranked and filtered
- Clean context is prepared
- Context is injected into the prompt
- AI model generates a response
- Response is validated and delivered
Thus, generation always happens after retrieval, not before.
Core Components of Retrieval Augmented Generation Architecture
1. Data Sources Layer
First of all, RAG systems rely on external data sources.
These typically include:
- Documents (PDFs, HTML, Word files)
- Databases
- Knowledge bases
- APIs
- Enterprise systems
Therefore, the quality of a RAG system depends heavily on data quality and structure.
2. Ingestion and Indexing Layer
Next, raw data must be prepared for retrieval.
This layer performs:
- Text extraction
- Data cleaning
- Chunking large documents
- Metadata enrichment
- Indexing
- Embedding generation
As a result, data becomes searchable and retrievable.
3. Retrieval Layer
After indexing, the retrieval layer is responsible for fetching relevant information.
Modern RAG systems use:
- Keyword search
- Semantic (vector) search
- Hybrid retrieval (both combined)
Therefore, the system can retrieve both precise matches and conceptual matches.
4. Ranking and Filtering Layer
However, raw retrieval results are not always useful.
Because of this, a ranking and filtering layer is required.
This layer:
- Ranks results by relevance
- Removes duplicates
- Filters outdated content
- Applies access control rules
As a result, only high-quality content is passed to the AI model.
5. Context Assembly Layer
Next, retrieved content must be structured properly.
This includes:
- Ordering information logically
- Formatting content consistently
- Managing token limits
- Injecting system instructions
Therefore, the model receives clean, relevant, and structured context.
6. Generation Layer
At this stage, the AI model generates a response using:
- User query
- Retrieved context
- System instructions
In advanced systems, multiple models may be used for:
- Reasoning
- Summarization
- Extraction
As a result, performance and cost are optimized.
7. Validation and Post-Processing Layer
Finally, enterprise-grade RAG systems apply validation.
This may include:
- Rule-based checks
- Confidence scoring
- Source citation
- Output formatting
- Compliance checks
Therefore, the final response becomes trustworthy and production-ready.
RAG Architecture vs Traditional AI Systems
| Feature | Traditional AI | RAG Architecture |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge source | Model memory | Real data |
| Accuracy | Unreliable | Grounded |
| Data freshness | Static | Dynamic |
| Explainability | Low | High |
| Scalability | Limited | Enterprise-grade |
Thus, RAG architecture clearly outperforms standalone model systems.
Types of RAG Architectures
Single-Stage RAG
Simple retrieval followed by generation. Suitable for small-scale applications.
Multi-Stage RAG
Multiple retrieval and ranking steps. Used in enterprise systems.
Agentic RAG
Retrieval is dynamically triggered by AI agents during reasoning.
Each architecture trades simplicity for control and scalability.
Enterprise Use Cases of RAG Architecture
RAG architecture is widely used in:
- Enterprise knowledge systems
- Customer support automation
- Research and analytics platforms
- Compliance and legal systems
- Internal documentation search
In every case, RAG ensures accuracy, trust, and reliability.
Engineering Challenges in RAG Architecture
However, building RAG systems introduces challenges.
These include:
- Data quality management
- Retrieval accuracy tuning
- Latency optimization
- Prompt size limits
- Evaluation and monitoring
Therefore, strong system engineering is essential.
Best Practices for RAG Architecture in 2026
To build reliable RAG systems:
- Separate retrieval and generation layers
- Use hybrid retrieval strategies
- Apply strict filtering and ranking
- Limit context aggressively
- Validate outputs before action
- Monitor retrieval quality continuously
As a result, systems remain scalable and trustworthy.
The Future of Retrieval Augmented Generation Architecture
Looking ahead, RAG architecture will continue to evolve.
Future systems will feature:
- Adaptive retrieval strategies
- Self-optimizing pipelines
- Multi-agent collaboration
- Autonomous validation loops
- Deeper workflow integration
Therefore, RAG will become the core backbone of enterprise AI infrastructure.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, Retrieval Augmented Generation architecture is the foundation of modern, reliable AI systems.
By separating knowledge retrieval from language generation, RAG enables AI systems that are:
- Accurate
- Explainable
- Scalable
- Governed
- Enterprise-ready
In 2026, successful AI platforms are not defined by the models they use, but by how well retrieval and generation are architected together.
RAG architecture is no longer an innovation — it is a necessity.
