Generative AI has moved far beyond experimentation. In 2026, organizations are no longer asking “Can AI generate answers?” — they are asking “Can AI generate answers we can trust?”
This shift has brought Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) into the mainstream. But as real-world adoption increases, a new layer has become critical: RAG orchestration.
Without orchestration, RAG systems quickly become unreliable, slow, and difficult to govern. With orchestration, they evolve into scalable, production-ready AI systems capable of supporting enterprise workloads.
This article explains what RAG orchestration is, why it matters, how it works, and how modern AI systems use it in 2026.
What Is RAG Orchestration?
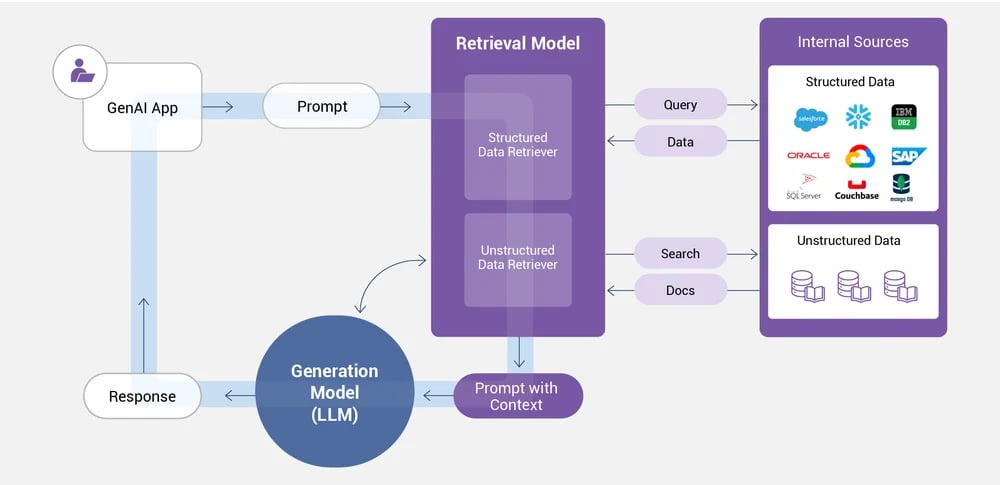
RAG orchestration is the structured coordination of retrieval, reasoning, and generation workflows inside an AI system.
Instead of a simple pipeline like:
Query → Retrieve documents → Send to LLM → Answer
Orchestrated RAG systems introduce decision-making logic at every stage:
Query → Intent detection → Source selection → Retrieval → Ranking → Context filtering → Model selection → Generation → Validation → Response
In simple terms, RAG orchestration decides how and when retrieval and generation should happen, rather than treating them as a single static step.
Why Basic RAG Fails at Scale
Early RAG implementations worked well for demos and prototypes, but they struggle in real environments.
Common issues with non-orchestrated RAG systems include:
- Retrieving irrelevant or outdated documents
- Sending too much context to the model
- Poor ranking of retrieved content
- No awareness of user intent
- No validation of model output
- High latency and cost
As usage grows, these problems compound. RAG orchestration exists to solve these failures systematically.
Core Objectives of RAG Orchestration
RAG orchestration is not about complexity for its own sake. It exists to achieve four clear goals:
- Accuracy – Retrieve the right information
- Efficiency – Minimize unnecessary model calls and context
- Control – Enforce rules, permissions, and validation
- Scalability – Support real-world workloads reliably
These goals define how modern AI platforms are designed in 2026.
Key Components of a RAG Orchestration Layer


1. Query Understanding and Intent Classification
Before retrieval begins, orchestrated systems analyze the user query to determine:
- Is this a simple factual lookup?
- Does it require comparison?
- Is it a multi-step reasoning task?
- Does it need real-time or historical data?
This step ensures the system chooses the correct retrieval strategy instead of treating every query the same way.
2. Dynamic Source Selection
Enterprise data is distributed across multiple systems.
RAG orchestration dynamically selects sources such as:
- Document repositories
- Databases
- Knowledge bases
- APIs
Instead of querying everything, the orchestrator targets only relevant sources, improving both speed and accuracy.
3. Retrieval Strategy Management
Different queries require different retrieval approaches.
Orchestration enables:
- Keyword search for precise terms
- Semantic search for conceptual queries
- Hybrid retrieval for mixed use cases
The orchestrator decides which retrieval method to apply and when.
4. Ranking, Filtering, and Deduplication
Raw retrieval results are rarely prompt-ready.
Orchestrated RAG systems:
- Rank results by relevance
- Remove duplicates
- Filter low-confidence content
- Select only the most useful chunks
This avoids the common problem of overloading the model with noise.
5. Context Packaging and Prompt Assembly
Once content is selected, it must be structured properly.
RAG orchestration:
- Orders context logically
- Applies formatting rules
- Injects system instructions
- Controls token usage
This step has a major impact on response quality and consistency.
6. Model Selection and Generation
In 2026, many systems use multiple models.
Orchestration decides:
- Which model handles reasoning
- Which model handles summarization
- When to fall back to simpler models
This approach balances cost, speed, and accuracy.
7. Validation and Post-Processing
Enterprise systems cannot rely solely on probabilistic output.
RAG orchestration may include:
- Rule-based validation
- Confidence scoring
- Source citation enforcement
- Response formatting
Only validated outputs are returned or acted upon.
RAG Orchestration vs Traditional Pipelines
| Feature | Basic RAG | Orchestrated RAG |
|---|---|---|
| Retrieval | Single step | Multi-stage |
| Context control | Minimal | Strict |
| Accuracy | Inconsistent | High |
| Governance | Limited | Built-in |
| Scalability | Low | Enterprise-grade |
This difference is why orchestration is now considered mandatory for serious AI systems.
RAG Orchestration and Agentic AI
Agentic AI systems rely heavily on RAG orchestration.
Agents:
- Break tasks into steps
- Request information multiple times
- Evaluate intermediate results
RAG orchestration ensures agents:
- Retrieve correct data at each step
- Avoid redundant queries
- Maintain context across actions
Without orchestration, agent-based systems become unpredictable and expensive.
Common Use Cases for RAG Orchestration
Enterprise Knowledge Systems
Employees query internal knowledge and receive accurate, source-grounded answers.
Research and Analysis
Systems analyze large document sets, compare findings, and synthesize insights.
Customer Support Automation
AI retrieves user-specific data before generating responses.
Compliance and Risk Monitoring
Automated analysis of policies and regulations with explainable outputs.
Engineering Challenges in RAG Orchestration
Building orchestrated RAG systems introduces challenges such as:
- Managing latency across multiple steps
- Maintaining data freshness
- Monitoring retrieval quality
- Handling prompt size limits
- Evaluating end-to-end accuracy
These challenges require software engineering discipline, not just ML expertise.
Best Practices for RAG Orchestration in 2026
- Separate retrieval and generation logic
- Limit prompt context aggressively
- Use hybrid retrieval when possible
- Validate outputs before action
- Monitor system performance continuously
RAG orchestration is best treated as a system architecture problem, not a prompt engineering problem.
The Future of RAG Orchestration
As AI systems mature, RAG orchestration is evolving toward:
- Adaptive retrieval strategies
- Self-optimizing pipelines
- Autonomous validation loops
- Deeper workflow integration
This evolution will enable AI systems to function as reliable, long-running services, not just conversational tools.
Final Thoughts
RAG orchestration is the layer that transforms generative AI from a powerful but unreliable tool into a trusted, scalable system.
In 2026, successful AI platforms are defined not by the models they use, but by how well retrieval, reasoning, and validation are orchestrated.
Organizations that invest in orchestrated RAG architectures gain:
- Higher accuracy
- Lower operational risk
- Better scalability
- Stronger governance
RAG orchestration is no longer optional — it is the foundation of modern AI systems.
